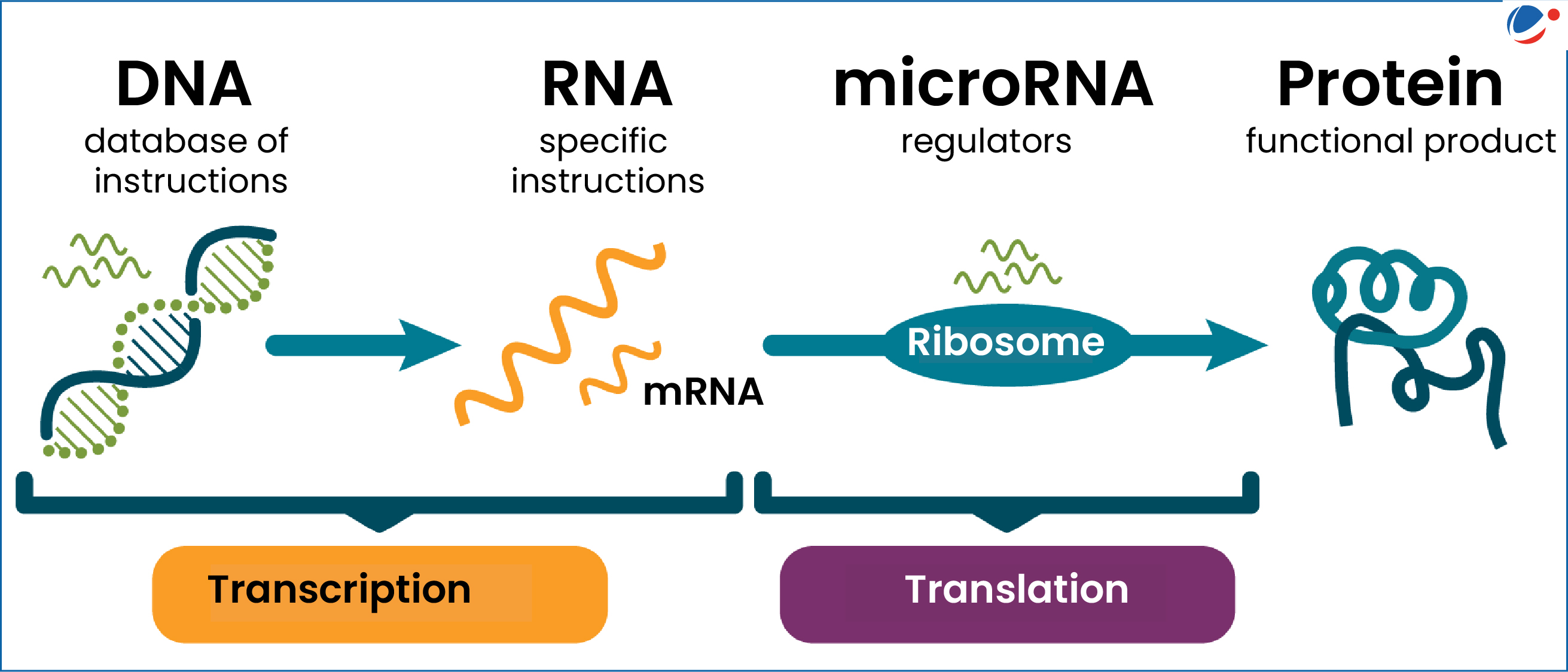
The groundbreaking discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s has transformed our understanding of gene regulation, ultimately leading to the pair receiving the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. This remarkable achievement highlights the significance of federal funding in research, which played a crucial role in supporting their innovative work. Initially met with skepticism, the discovery revealed that microRNAs are fundamental players in both plant and animal biology, influencing crucial processes like development and mature function. With increasing recognition, microRNA research has sparked interest in RNA therapeutics, paving the way for potential treatments for chronic diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. As researchers continue to explore the vast implications of microRNAs, they stand at the forefront of a revolution in molecular biology and therapeutic interventions.
The revelation of small RNA molecules, commonly known as microRNAs, marked a pivotal moment in the field of genetics, offering fresh insights into the mechanisms governing gene expression. Researchers, including the notable Gary Ruvkun, embarked on a journey that unveiled the intricate layers of cellular regulation. Despite initial indifference from the broader scientific community, the importance of these tiny regulatory RNAs has since gained recognition, leading to expansive research and funding. These molecular entities not only play a vital role in biological processes across diverse organisms, but they also hold promise for RNA-based therapies targeting critical health issues. As the field advances, the influence of microRNA discovery on biotechnology and medical science continues to expand, signifying a remarkable interdisciplinary frontier.
The Journey of MicroRNA Discovery
In the early 1990s, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros made a ground-breaking discovery that would later transform our understanding of genetic regulation through microRNA. This groundbreaking research, while not immediately recognized, laid the foundation for what would evolve into a significant field of study in molecular biology. Initially met with skepticism, the discovery revealed microRNAs as crucial regulators of gene expression, impacting everything from plant growth to human health. Their work demonstrated that these small RNA molecules play a pivotal role in translating genes into proteins, making them essential to developing and maintaining life.
Over the years, as research interest grew, the appreciation for microRNA’s role in gene regulation blossomed. Ruvkun and Ambros’s initial findings sparked discussions among evolutionary biologists, eventually drawing a diverse community of researchers. The burgeoning field highlighted that the implications of their discovery extended beyond C. elegans, affecting a myriad of organisms—including humans. By the time the decade ended, microRNAs had become a subject of intense research focus, revealing their involvement in complex diseases and normal cellular functions.
Federal Funding’s Impact on Scientific Research
The success of Gary Ruvkun’s laboratory and many like it can be attributed significantly to the federal funding they receive. For over four decades, a substantial portion of their research has been supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Ruvkun has pointed out that this investment not only sustains his laboratory’s operations but also contributes to a broader ecosystem of scientific advancement. As he emphasizes, scientific research financed by federal dollars leads to transformative discoveries that have far-reaching implications, including the development of RNA therapeutics designed to combat diseases ranging from cancer to Alzheimer’s.
However, there have been growing concerns about potential cuts to federal research funding, which could jeopardize future advancements in molecular biology and other critical fields. Ruvkun warns that a decline in funding could deter young scientists from pursuing research careers. The economic implications of this trend are profound; without a stable foundation of federal investment, the United States risks losing its competitive edge in biotechnology and related sectors, which have historically been driven by groundbreaking research.
The Revolutionary Role of MicroRNAs in Medicine
As research progressed, the significance of microRNAs in the medical field became increasingly evident. Studies have shown that these tiny regulatory molecules can control many genes, determining protein synthesis that is vital for nearly every biological function. With about 1,000 microRNAs identified in the human genome, their role in regulating disease pathways became a significant focus for developing therapeutic interventions. The discovery of microRNA has ushered in a new era where targeted therapies that harness RNA molecules are being explored for various diseases, including heart disease and cancer.
The clinical applications of RNA therapeutics are expanding rapidly, evidenced by ongoing trials aimed at bringing innovative treatments to patients. Pharmaceutical companies, notably Alnylam, have risen to prominence by specializing in RNA interference therapeutics, highlighting a direct economic impact stemming from foundational research in microRNA. This shift underscores the importance of continued investment in basic science, as it serves as the bedrock for medical advances that save lives and enhance the quality of healthcare globally.
Gary Ruvkun’s Contribution to Genetics
Gary Ruvkun has emerged as a pioneering figure in the field of genetics, largely due to his groundbreaking discovery of microRNA. His academic journey began at Harvard, where he collaborated with Victor Ambros to unveil the complexities of gene regulation through tiny RNA molecules. Their innovative work challenged existing paradigms and opened up new avenues for understanding biological systems at a molecular level. This significant contribution not only earned Ruvkun a prestigious Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 but also established him as a key player in shaping the future of genetic research.
Ruvkun’s insights on microRNA’s function have provided a deeper appreciation of RNA’s structural versatility and regulatory capabilities. By exposing the dynamic role of microRNAs within various biological contexts, he has laid the groundwork for future explorations of gene therapy and beyond. His ongoing commitment to research and education continues to inspire the next generation of scientists to embrace the field of genetics and pursue innovative solutions to complex health challenges.
The Shift in Scientific Interest Over Decades
When Ruvkun and Ambros first published their research on microRNAs in 1993, there was limited acknowledgment of its potential impact. The scientific community’s initial indifference slowly transformed as researchers began to observe the universality of microRNA functions across multiple organisms. As interest in the field blossomed, so did participation in conferences and meetings, signaling a shift in the scientific narrative surrounding RNA research. Ruvkun recalls a pivotal moment when gatherings that once included a mere 100 attendees began to fill with hundreds of eager participants, all drawn by the potential relevance of microRNAs.
This paradigm shift reflects a broader trend within molecular biology, where once-overlooked discoveries can rapidly gain traction and foster interdisciplinary collaboration. The realization that microRNAs hold key roles in gene regulation has brought together researchers from various backgrounds, including plant biology, developmental biology, and human medicine, fostering innovative projects that leverage the insights gained from Ruvkun and Ambros’s original work.
The Economic Impact of RNA Research
As the field of RNA research has expanded, it has had substantial economic implications, particularly through the emergence of companies dedicated to RNA therapeutics. Alnylam Pharmaceuticals serves as a prime example of how foundational research can propel the biotechnology industry forward. Established on the principles of RNA interference, Alnylam has grown to become one of Massachusetts’s leading companies, showcasing the potential of research funded by federal grants. Their focus on developing RNA-based therapies underscores a lucrative path that ties academic discoveries to tangible healthcare solutions.
The success of RNA therapeutics illustrates how investments in scientific research can ignite economic growth and innovation. As pharmaceutical companies begin to realize the therapeutic potential of microRNAs, new markets and job opportunities in the biopharmaceutical sector emerge. Ruvkun’s praises for federal funding highlight that such investments are not merely expenditures, but rather, they are crucial catalysts for job creation, economic stability, and the advancement of medical science.
Future Directions in MicroRNA Research
As we look to the future, the field of microRNA research is poised for remarkable advancements, driven by rapid technological innovations and a growing understanding of molecular mechanisms. Continued exploration of microRNA’s roles in gene regulation will likely yield more targeted therapies, improving treatment efficacy and patient outcomes. Researchers are optimistic about utilizing microRNA profiles as biomarkers for disease prediction and prognosis, enhancing personalized medicine strategies.
Moreover, the ongoing collaboration between academia and the biotech industry will be instrumental in translating microRNA discoveries into clinical applications. With advancing techniques in RNA editing and delivery systems, the next generation of RNA therapeutics aims not only to treat but potentially cure genetic diseases. As scientists build on the groundbreaking work initiated by Ruvkun and Ambros, the future holds great promise for harnessing microRNA’s potential to revolutionize healthcare.
The Legacy of Gary Ruvkun and MicroRNA Research
Gary Ruvkun’s legacy in the scientific community is underscored by his pivotal role in the discovery of microRNA and its implications for gene regulation. His journey from obscurity to receiving the 2024 Nobel Prize illustrates a remarkable evolution in the perception of RNA research over the past three decades. Ruvkun’s commitment to basic research has not only advanced our understanding of genetic regulation but also paved the way for novel therapeutic strategies that could change lives.
As Ruvkun continues to mentor emerging scientists, his influence will undoubtedly shape the next generation’s approach to genetic research. His work has inspired countless researchers to dive deeper into the mysteries of RNA, fostering an environment where innovation is encouraged and excellence is pursued. The ongoing exploration of microRNA and its applications is a testament to Ruvkun’s enduring impact on the scientific landscape, ensuring that his contributions resonate well into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microRNA discovery and why is it important?
MicroRNA discovery refers to the identification and understanding of microRNAs, which are small, non-coding RNA molecules that play crucial roles in gene regulation. Discovered by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s, microRNAs are essential for controlling the expression of genes in various organisms, including humans. Their significance lies in their ability to influence cellular processes and development, making them key players in research related to RNA therapeutics, cancer treatment, and other diseases.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to the field of microRNA discovery?
Gary Ruvkun, alongside Victor Ambros, was instrumental in the microRNA discovery that earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Their pioneering research revealed the regulatory functions of microRNAs in the model organism C. elegans. This groundbreaking work has not only reshaped our understanding of gene regulation but has also paved the way for the development of RNA therapeutics targeting conditions like heart disease and cancer.
What role does federal funding play in microRNA research?
Federal funding has been essential for advancing microRNA research, with researchers like Gary Ruvkun receiving consistent support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) over the past few decades. This financial backing has enabled significant discoveries in gene regulation and laid the groundwork for crucial developments in RNA therapeutics, highlighting the importance of governmental support in scientific research.
How has microRNA discovery influenced RNA therapeutics?
The discovery of microRNAs has had a profound impact on RNA therapeutics, leading to innovative treatments for various diseases. These small RNA molecules regulate gene expression, and understanding their mechanisms has opened doors to developing therapies that can manipulate gene activity to combat conditions such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease. This has made microRNA a focal point of research in gene therapy.
What are the implications of microRNA discovery for human health?
MicroRNA discovery has significant implications for human health as it assists in the understanding of gene regulation mechanisms that underlie many diseases. The research by Gary Ruvkun and others has identified approximately 1,000 microRNAs in the human genome that regulate gene expression, influencing disease processes and offering new avenues for RNA therapeutics development aimed at improving health outcomes.
What challenges does microRNA research face in terms of funding?
Despite the groundbreaking discoveries in microRNA research, challenges remain regarding funding. Gary Ruvkun emphasizes the need for sustained federal support for scientific research, as fluctuations in funding can impact the capability of laboratories to continue exploring essential topics like microRNA and their applications in RNA therapeutics. Without adequate funding, promising young researchers may seek opportunities outside the United States.
How can microRNA discovery contribute to future scientific advancements?
MicroRNA discovery serves as a cornerstone for future scientific advancements by enhancing our understanding of gene regulation and opening new research pathways. As more is learned about the roles of microRNAs in various biological processes and diseases, advancements in RNA therapeutics may lead to innovative treatments and strategies in precision medicine, benefiting healthcare on a global scale.
What can we learn from the journey of microRNA discovery over the years?
The journey of microRNA discovery teaches us about perseverance in scientific research. Initially, Ruvkun and Ambros faced skepticism from the scientific community; however, their work gradually gained recognition, illustrating how pivotal and revolutionary discoveries can take time to be accepted. Their experiences also underscore the critical role of federal funding in transforming groundbreaking research into practical applications.
| Year | Discoverers | Key Discoveries | Funding Source | Impact | Current Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros | Discovered microRNA in C. elegans | NIH grants | Key role in gene regulation across species | Increasing interest in RNA research, especially microRNAs, from various fields. |
| 1993 | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros | Published findings in Cell journal | NIH funding | Helped establish foundational RNA science | Substantial genomic and therapeutic research leading to clinical trials. |
| 2024 | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros | Awarded Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine | Federal research funding | Validation of microRNA’s role and importance in biology | Development of therapeutics targeting microRNAs for diseases. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation since its inception in the 1990s. The groundbreaking work of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros has paved the way for significant advancements in molecular biology, illustrating how tiny RNA molecules play critical roles in gene expression across various organisms. Their diligent research, supported by federal funding, has not only earned them recognition, exemplified by the 2024 Nobel Prize, but has also sparked a surge of interest in therapeutic applications. As microRNA research continues to evolve, it holds immense potential for addressing diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, promising a new era of targeted treatments.