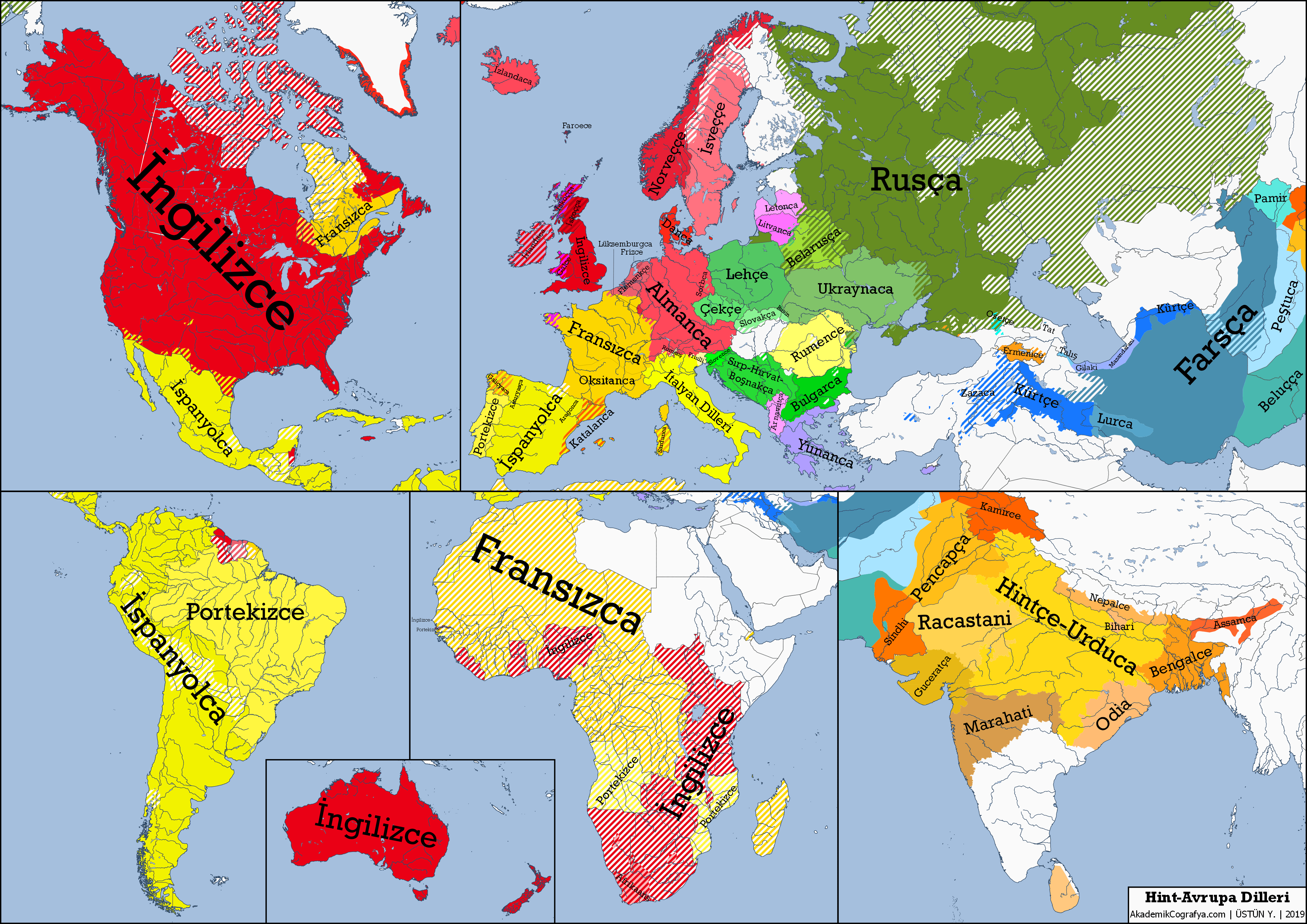
Indo-European languages encompass a vast family of over 400 languages, spoken by nearly 40% of the global population. Recent genetic research has unraveled the origins of this influential language group, pinpointing the Caucasus Lower Volga people in present-day Russia around 6,500 years ago as their earliest speakers. This discovery shines a light on the Yamnaya people, who played a critical role in disseminating these languages across Europe and Asia. Archaeological findings have revealed that these ancient communities not only shared a common linguistic ancestry, but also participated in a profound cultural mixing that shaped the languages we recognize today. By tracing language origins through genetic lineage, researchers are piecing together a narrative that connects ancient peoples with their modern descendants.
The study of Indo-European languages, often referred to as the ancestral tongues of a significant portion of humanity, reveals intriguing connections among cultures across vast geographic regions. Linguists and archaeologists have long explored the roots of these languages, seeking clues from the Yamnaya civilization and their migration patterns into Europe and beyond. These early populations, embedded in the context of Eurasian history, contributed to the linguistic tapestry woven by their descendants throughout generations. Delving into the genetic research allows for a deeper understanding of how language and identity evolved—transforming not only how we communicate, but also how we perceive human connectivity across historical timelines. Through this lens, the origins and migrations of these early language speakers illuminate the rich and diverse heritage of humanity.
Understanding the Origins of Indo-European Languages
The origins of Indo-European languages, which now encompass over 400 distinct languages globally, have puzzled linguists for centuries. Recent studies utilizing genetic research have shed light on this historical mystery, particularly focusing on the Caucasus Lower Volga region. The research suggests that speakers of the ancestor tongue lived approximately 6,500 years ago in what is now Russia. These findings align closely with the steppe hypothesis, which proposes that the Indo-European languages can be traced back to the fascinating intercultural exchanges that occurred in this area during the Eneolithic period.
The identification of the Caucasus Lower Volga people as the progenitors of this language family highlights the profound impacts of migration and genetic intermingling. As nomadic pastoralists, these individuals not only spread their linguistic heritage but also their cultural practices across vast territories from the Black Sea to as far west as Ireland. This transformative journey demonstrates how language evolution is deeply intertwined with the migrations of people and their adoption of new trading practices, like herding and agriculture.
The Role of the Yamnaya People in Language Evolution
Central to the narrative of Indo-European languages is the Yamnaya people, who are believed to have played a critical role in shaping the linguistic landscape of Europe and beyond. These nomadic tribes, characterized by their distinct burial practices and advanced use of technology such as horse-drawn wagons, had far-reaching influences on neighboring cultures. Their movement through the steppe regions not only facilitated the spread of their Indo-European tongue, but also integral cultural practices that were absorbed by local populations.
Archaeological findings related to the Yamnaya illustrate their crucial position in the historical timeline of language development. They were among the first to exploit the expansive Eurasian grasslands, effectively enabling a demographic explosion that allowed their languages to permeate various regions. As scholars analyze the genetic footprints left by the Yamnaya, they simultaneously reconstruct the pathways through which language evolved and diversified across Europe, marking the advent of proto-Indo-European as a significant milestone in human history.
Genetic Research: The Bridge to Understanding Language Origins
Genetic research has revolutionized our understanding of ancient populations and their migration patterns, particularly regarding the origins of Indo-European languages. With advanced techniques like DNA analysis, researchers have traced the genetic lineages of the Caucasus Lower Volga people who are believed to be pivotal in the early dissemination of these languages. This genetic evidence not only corroborates archaeological findings but also provides a clearer picture of how cultural and linguistic traditions interconnect.
The studies conducted by teams including Harvard researchers highlight the synergy between linguistics and genetic research. By combining data from various ancient DNA samples, scholars can outline the migration routes and interactions between early Indo-European speakers and neighboring populations. This comprehensive approach enhances our understanding of how languages evolved, revealing that the development of Indo-European languages was a dynamic process influenced by multiple migrations and cultural exchanges.
Cultural Practices and Linguistic Development Among Early Populations
Language does not exist in a vacuum; it is deeply rooted in cultural practices and social interactions. The Yamnaya people, associated closely with the Caucasus Lower Volga region, demonstrate this intertwining of language and culture through their burial customs and lifestyle choices. The kurgans, or burial mounds, signify a profound connection to their identity and community, cementing their cultural footprints throughout history. Such practices play a significant role in the preservation and transmission of languages.
As researchers delve into the archaeological findings surrounding these ancient burial sites, they discover not only artifacts but also insights into the complex socio-linguistic landscape of early Indo-European societies. The influence of these cultural traditions can be seen in the languages spoken by descendants of the Yamnaya, enriching our understanding of how shared practices and language development evolved in tandem over millennia.
The Archaeological Evidence of Indo-European Language Expansion
Archaeological findings are crucial to understanding the expansion of Indo-European languages. Excavations across the Eurasian steppes have revealed significant artifacts that suggest a complex interplay of migration, trade, and cultural exchange. The artifacts, including pottery and tools associated with the Yamnaya culture, indicate that these populations were not merely nomadic but actively engaged in interacting with other cultures, facilitating the diffusion of their language.
These material remnants serve as tangible evidence of how language and culture were transmitted across generations and geographies. As archaeologists continue to uncover these finds, they create a clearer narrative of how the Indo-European languages spread from the steppe regions and established roots in Europe, Asia, and beyond, further enhancing the field of historical linguistics.
The Genetic Legacy of Proto-Indo-European Speakers
The genetic legacy left by proto-Indo-European speakers, particularly the Yamnaya people, has profound implications for understanding modern populations. Not only did the Yamnaya contribute to linguistic traditions, but their genetic lineage can be traced through various European countries, showcasing the extensive reach of their genetic influence. Research indicates that a significant percentage of modern Europeans carry DNA linked to these ancient populations, highlighting their role in shaping contemporary identities.
By studying the genetic variations and relationships among current populations, researchers can uncover the intricate history of migrations and expansions associated with the Indo-European languages. This genetic reconstruction provides a clearer framework for understanding how languages evolved and diversified over centuries, leading to today’s rich tapestry of languages spoken worldwide.
Indo-European Language Family: A Global Perspective
The Indo-European language family represents one of the largest and most widespread linguistic groups in the world. With languages spoken by nearly 40% of the global population, understanding their origins and development is essential for linguists and historians alike. The story began millennia ago with the Caucasus Lower Volga people, whose descendants spread their language across vast regions, influencing countless civilizations along the way.
From the Romance languages derived from Latin to the Germanic languages of Northern Europe, the reverberations of early Indo-European languages can be felt today across continents. This global perspective has prompted linguists to explore not just the linguistic aspects but also the social, cultural, and genetic dimensions of how these languages developed and transformed over time.
Challenges in the Study of Indo-European Languages
Despite advancements in genetic analysis and archaeological research, studying the origins and spread of Indo-European languages presents certain challenges. The geopolitical tensions, notably between Russia and Ukraine, complicate collaborative research efforts that are vital for a comprehensive understanding of the subject. The inability to share findings and assemble complete data sets restricts the scope of research; nonetheless, the existing data provides invaluable insights.
Moreover, as researchers navigate the intricacies of linguistics, genetics, and archaeology, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of their findings remains paramount. Utilizing modern technologies and fostering international collaborations will be essential in overcoming these hurdles and deepening our understanding of the Indo-European language family.
Future Directions in Indo-European Studies
The future of Indo-European studies appears promising, given the continuous advancements in genetic research and archaeological methodologies. As new technologies emerge, researchers can delve deeper into the historical contexts of language development and migration. Innovations such as genome-wide association studies and ancient DNA analyses will likely unveil further connections between linguistic development and population genetics.
Moreover, interdisciplinary approaches that encompass genetics, archaeology, and linguistics will foster a more holistic understanding of how Indo-European languages evolved and influenced various civilizations. By combining diverse fields of study, scholars can address existing gaps in knowledge and build upon the significant findings of notable researchers to establish a comprehensive narrative of Indo-European language origins.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Caucasus Lower Volga people in the study of Indo-European languages?
The Caucasus Lower Volga people are considered the originators of Indo-European languages, as recent genetic research has traced their lineage back to present-day Russia around 6,500 years ago. This discovery integrates archaeological findings and supports the steppe hypothesis, highlighting their role in the cultural and linguistic evolution that led to the spread of over 400 Indo-European languages.
How did the Yamnaya people contribute to the development of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya people, emerging from the Caucasus Lower Volga, played a crucial role in the expansion of Indo-European languages by migrating across vast territories from the Eurasian steppes to Europe and Asia. Genetic studies show that they carried their languages and cultural practices, which significantly transformed populations in Europe and beyond.
What role does genetic research play in understanding the origins of Indo-European languages?
Genetic research has been pivotal in tracing the ancestry of Indo-European languages back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya culture. By analyzing DNA from ancient populations, researchers can identify migration patterns, the intermingling of cultures, and how languages spread, thus providing a clearer picture of linguistic origins.
What archaeological findings support the theories about the Yamnaya and Indo-European language origins?
Archaeological findings suggest that the Yamnaya people buried their dead in kurgans, similar to their Caucasus Lower Volga ancestors. These burial practices and artifacts found at ancient sites reinforce the connection between these groups and support theories about the spread of Indo-European languages across Europe and into Asia.
What are the implications of the connection between the Yamnaya and ancient Anatolian languages on our understanding of Indo-European languages?
The connection between the Yamnaya and ancient Anatolian languages highlights the complex migration and evolution of Indo-European languages. It suggests that while the Yamnaya contributed significantly to the spread of these languages in Europe, early branches like the Anatolian languages diverged earlier, indicating a more intricate web of linguistic development than previously understood.
How have historical events affected contemporary research on Indo-European languages?
Contemporary research on Indo-European languages faces challenges due to geopolitical issues, particularly the Russia-Ukraine war, which has complicated collaborative studies. Researchers rely on ancient DNA from both Russian and Ukrainian archaeological sites to piece together the origins and migration of Indo-European languages while navigating these current conflicts.
What impact did the Yamnaya’s mobility have on the distribution of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya’s advanced mobility, facilitated by their use of horseback riding and oxen-towed wagons, allowed them to spread their culture and language widely across Eurasia. This unprecedented movement enabled their languages to influence regions as far apart as Mongolia and Ireland, contributing to the globalization of the Indo-European language family.
Why is the study of the origins of Indo-European languages important today?
Studying the origins of Indo-European languages is crucial for understanding human history, culture, and migration. It reveals how ancient populations interacted, influenced one another, and contributed to the linguistic diversity seen in 40% of the world’s languages today, thereby enriching our comprehension of human communication and cultural evolution.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European Languages | Identified as originating from the Caucasus Lower Volga people in Russia around 6,500 years ago. |
| Research Findings | Landmark studies published in Nature journal unveil the genetic ancestry linking over 400 languages spoken by 40% of the world’s population. |
| Cultural Interactions | The genetic evidence shows intermingling with other populations, contributing to cultural traditions spread across the steppe. |
| Historical Background | The Yamnaya people, previously suggested candidates for the ancestors of Indo-European speakers, had significant roles in spreading these languages. |
| Genetic Reconstruction | The research includes ancient DNA samples from various regions, enhancing our understanding of language development and migrations. |
| Challenges in Research | Current geopolitical tensions complicate collaborative efforts among researchers studying the Indo-European languages. |
| Cultural Practices | The Yamnaya inherited burial traditions from their ancestors, reflecting their cultural continuity. |
Summary
Indo-European languages have a fascinating origin story rooted in the cultures of the Caucasus Lower Volga people of Russia approximately 6,500 years ago. Recent genetic studies have underscored the complex interactions and migrations that shaped the spread of these languages across vast regions, connecting over 400 distinct languages spoken by nearly half of the world’s population today. Understanding the journey of the Indo-European languages not only unravels a linguistic mystery but also illuminates the intricate tapestry of human history and cultural evolution.